OIDC authentication overview
On Bitrise, OIDC enables your builds to authenticate to external systems (such as AWS, GCP, Azure, container registries, secret management or artifact stores) without embedding long-lived credentials in your Workflows.
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an identity authentication protocol based on the OAuth 2.0 framework. It allows third-party applications to verify the identity of the end user, including using Single Sign-On across applications.
OIDC works by issuing JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) that provide information about the authentication operation's outcome and about the user's identity. The data about the authentication outcome and the user information are called claims.
The service that receives the token evaluates the token's claims against its OIDC policy. If the token's claims match the policy, the request is permitted; if they don't, it is rejected.
On Bitrise, OIDC enables your builds to authenticate to external systems (such as AWS, GCP, Azure, container registries, secret management or artifact stores) without embedding long-lived credentials in your Workflows. Bitrise can mint one or more identity tokens tied to a specific build, with claims such as a build number, commit hash, repository slug, app slug, or Workflow name.
These tokens are:
-
Issued for a particular build interaction so third-party services can grant access scoped only to that run.
-
Short-lived to minimize the consequences of potential exposure.
-
Consumable by federated services that accept OIDC: for example, you can exchange a Bitrise OIDC token for temporary cloud credentials.
Request an identity token for your build
To use an OIDC token to authenticate to a service from a Bitrise build, you need to fetch the token and then perform the credential exchange with the service. Bitrise offers Steps that handle parts of the process.
Get OIDC Identity Token Step
Use an OIDC token in your build for any service with the Get OIDC Identity Token Step. This Step lets your Workflows and Pipelines request temporary, auditable access to cloud resources or external services at runtime, without storing secrets in the repository or build configuration.
Set the Token audience input to configure the Step. This could be the URL of the service you want to access with the token or a specific identifier provided by the service.
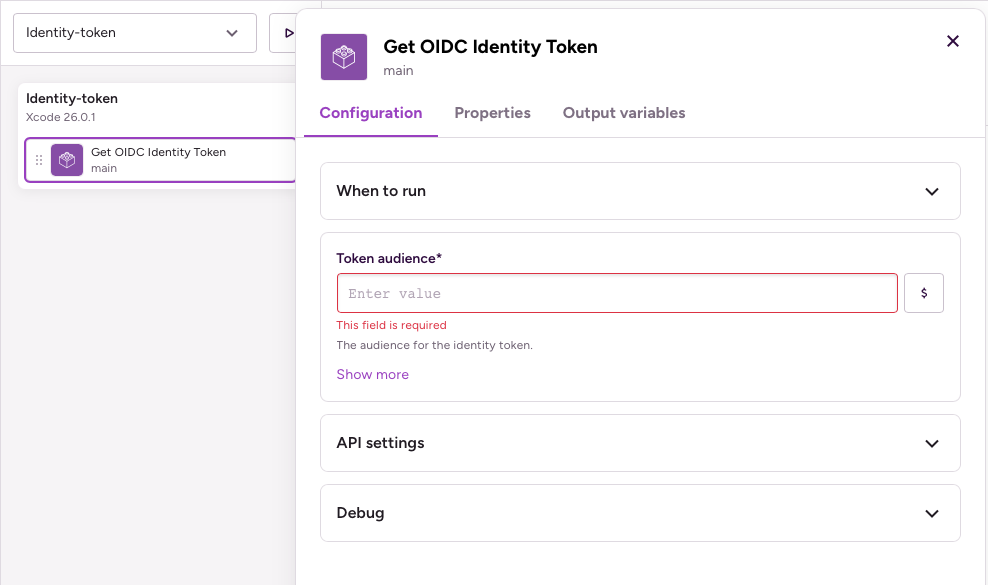
The Step exports an Environment Variable with the key BITRISE_IDENTITY_TOKEN, containing the relevant information of the token. Use it to exchange credentials with the service you want to access.
Dedicated Steps for specific services
The Get OIDC Identity Token Step lets you fetch an OIDC token for any service but it doesn't perform the credential exchange for you. For some services, we have Steps that take the care of the whole process:
-
Authenticate with Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Generates a Google auth token using a service account key, and authenticates to GCP.
-
Authenticate with Amazon Web Services (AWS): Generates an identity token based on an AWS IAM identity provider. You can read our full guide here: OIDC for AWS.
Information in the OIDC token
Bitrise includes the following information in the OIDC token:
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
Customisable audience field |
|
|
Who triggered the id token creation Note: It will be in the |
|
|
The token expiration time |
|
|
The time of the token generation |
|
|
Who issued the token |
|
|
Token unique identifier |
|
|
The current time |
|
|
Git commit hash |
|
|
The url of the app's associated git repo |
|
|
The git repository owner |
|
|
Git repository slug |
|
|
App slug |
|
|
Workspace slug |
|
|
What entity triggered the build |
|
|
The branch that is getting built |
|
|
PR target branch |
|
|
The tag which triggered the build |
|
|
Build number |
|
|
Name of the triggered workflow |